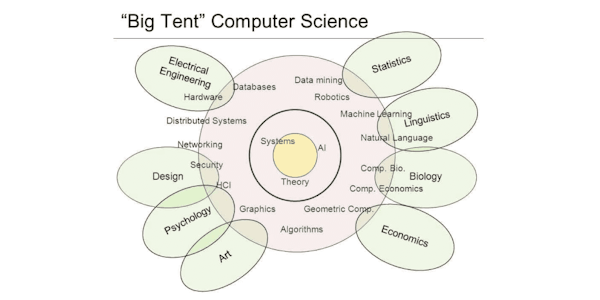
Across industries, data science is becoming an ever-increasing necessity for organizations to be successful. Collecting, analyzing and strategically acting on big data sets based on key signals is critical, and data scientists are the ones leading the way and informing decision makers.
This online Intermediate-level program is designed for working adults looking to pursue a career as a data scientist and roles focused on machine learning. Whether you already work with data in your current role or are interested in the larger field of computer science, this program is designed to build a solid foundation in underlying algorithms and principles of the tools used. This Foundational Data Science MicroBachelors program consists of two courses that develop key mathematical skills and explores terminology, models, and algorithms found in signal processing and machine learning.
With the successful completion of this program, passing all courses with a 70% or better via the verified (paid) track, you’ll not only receive a certificate highlighting your achievement, but also have the option to collect real college credit (included in the price!) that you can count towards a pursuit of a bachelor’s degree.
Prerequisite - In addition to the math skills developed in the Linear Algebra course, calculus (which is not a part of this program) is required.
Coaching
If you are enrolled in the verified track (paid track) in any course that is a part of a MicroBachelors program, including this course, you are eligible for coaching at no additional cost. Please note that coaching is only available via SMS to U.S. phone lines.
Our coaches (real humans) are ready to help you with career exploration, navigating resources, staying motivated, and solving problems along the way to your goals.
Learn more about the value of coaching directly from one of our coaches, Erin.